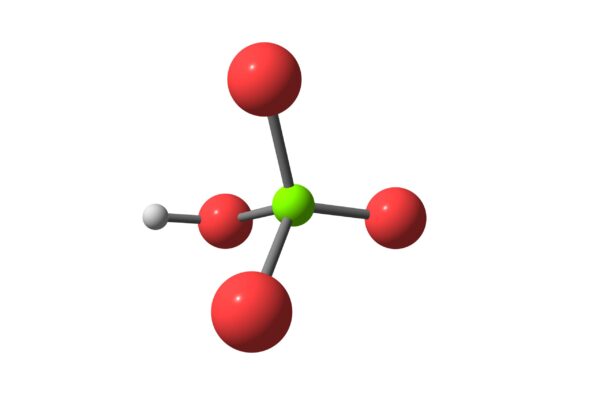
Perchloric Acid
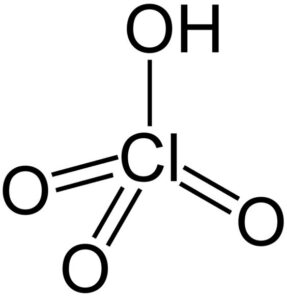
Perchloric Acid (HClO₄) is a highly reactive and strong acid known for being one of the strongest acids in chemistry. It is also a powerful oxidizer, especially at high concentrations. Due to its reactive and hazardous nature, it has specific industrial and laboratory applications, though it must be handled with great care.
Perchloric Acid (HClO₄) is a highly reactive and strong acid known for being one of the strongest acids in chemistry. It is also a powerful oxidizer, especially at high concentrations. Due to its reactive and hazardous nature, it has specific industrial and laboratory applications, though it must be handled with great care.
Chemical Properties:
- Chemical Formula: HClO₄
- Molecular Weight: 100.46 g/mol
- Density: 1.768 g/cm³ (at 25°C for 70% solution)
- Melting Point: -112°C (for anhydrous perchloric acid)
- Boiling Point: 203°C (for anhydrous perchloric acid)
- Solubility: Miscible in water, soluble in alcohols and ethers.
Physical Characteristics:
- Appearance: Colorless, odorless, fuming liquid (in concentrated form).
- pH: Extremely low pH, making it a superacid (stronger than sulfuric and nitric acids).
Concentrations:
- 70% Concentration: The most common form, which is highly corrosive but still manageable for many industrial and laboratory applications.
- Anhydrous Perchloric Acid (100%): Very reactive and unstable, and a powerful oxidizer.
Reactivity:
- Oxidizing Properties: At high temperatures and concentrations, perchloric acid is a strong oxidizer and can cause combustion or explosions if it comes into contact with organic materials.
- Non-oxidizing at Room Temperature: When diluted (below 70%), it behaves like a typical strong acid without significant oxidizing effects.
Common Uses:
- Laboratory Applications:
- Analytical Chemistry: Perchloric acid is used as a strong acid in titration methods, especially for acid-base titrations in analytical chemistry.
- Digestion of Samples: It is used for the preparation (digestion) of samples, especially in geochemistry, by breaking down complex substances to simpler forms.
- Perchlorate Salts: It is used to prepare perchlorate salts like potassium perchlorate, which are widely used in pyrotechnics and as oxidizers in propellants.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Perchloric acid is used in certain pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, often to aid in the production of drugs or intermediates that require strong acid conditions.
- Electrolyte in Batteries:
- Electrolytes: Perchloric acid or its salts (like lithium perchlorate) are used in high-energy batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries, due to their ability to conduct ions efficiently.
- Metallurgy:
- Etching and Polishing: It is used in metallurgical processes for etching metals and polishing surfaces due to its strong corrosive properties.
- Catalyst:
- Organic Synthesis: It acts as a catalyst in certain organic reactions, promoting faster and more efficient chemical transformations, particularly in esterification reactions.
Health and Safety Considerations:
- Safety:
- Highly Corrosive: Perchloric acid can cause severe chemical burns if it comes into contact with skin or eyes. It requires protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and acid-resistant clothing, during handling.
- Fuming Properties: Concentrated perchloric acid produces fumes that can cause severe irritation to the respiratory tract if inhaled.
- Toxicity:
- Inhalation Hazard: Fumes from perchloric acid can cause respiratory problems and should be handled in a fume hood.
- Ingestion: Ingesting perchloric acid can be fatal, leading to severe damage to the digestive system.
- Explosive Hazard:
- Oxidizer: At high concentrations or elevated temperatures, perchloric acid can act as an explosive oxidizer, especially in the presence of organic materials. Anhydrous perchloric acid, in particular, is extremely hazardous and must be handled with extreme caution.
- Environmental Impact:
- Water Contamination: Due to its extreme acidity, perchloric acid can cause significant harm to aquatic life if released into water bodies.
- Proper Disposal: It must be neutralized and disposed of according to strict regulations to avoid environmental damage.
Storage and Handling:
- Storage: Perchloric acid should be stored in dry, tightly sealed containers made of materials resistant to strong acids, like Teflon or glass. It must be kept away from heat, organic materials, and incompatible chemicals, particularly reducing agents and combustibles.
- Handling: It should only be handled in well-ventilated areas or under a fume hood due to its hazardous fumes. When working with perchloric acid, always wear proper PPE (gloves, goggles, and acid-resistant aprons).
Applications in Industry:
- Rocket Propellants:
- Perchlorates, derived from perchloric acid, are key components in solid rocket propellants. They serve as powerful oxidizing agents to support combustion in rockets.
- Explosives and Pyrotechnics:
- Perchloric acid is used in the production of perchlorate salts, such as ammonium perchlorate, which are used in explosives and pyrotechnics due to their strong oxidizing ability.
- Electronics and Semiconductors:
- In the electronics industry, perchloric acid is used in etching processes to clean and prepare metal surfaces in the manufacturing of semiconductors.
Handling and Safety Precautions:
- Never Mix with Organic Materials: Mixing perchloric acid with organic substances can result in spontaneous combustion or explosion.
- Dilute Slowly: When diluting perchloric acid, always add the acid to water slowly, as it can react violently if improperly mixed.
- Use in Fume Hoods: Due to its hazardous fumes, especially when concentrated, perchloric acid should be handled in fume hoods with proper ventilation.
- Avoid Heat: Keep perchloric acid away from sources of heat, as it can become highly reactive at elevated temperatures.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.